1. Grundlagen¶
1.1. Daten¶
Daten eintragen¶
Als Python-Liste
keine Rechenoperationen möglich
x = [0,1,2,3,4]
y = [2,4,1,5,3]
y2 = [4,2,5,1,0]
Als numpy-Array
import numpy as np
x = np.array([0,1,2,3,4])
y = np.array([2,4,1,5,3])
y2 = np.array([4,2,5,1,0])
Als pandas-dataframe
Die Werte für
xwerden dann mitdf["x"]abgerufen
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'x':[0,1,2,3,4], 'y1':[2,4,1,5,3], 'y2':[4,2,5,1,0]})
1.3. Scatter/Linien Plot¶
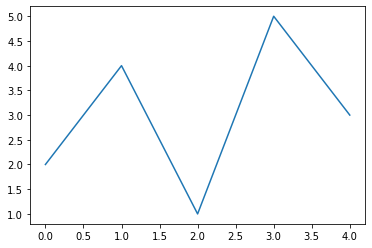
plt.plot(x,y);
Linien (Typ , Farbe , Dicke)¶
ls - Linienstil

c - Linienfarbe

lw - Liniendicke
default=1
Bilder aus: offizielle CheatSheets von Nicolas P. Rougier
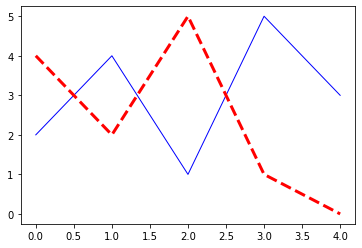
plt.plot(x,y,ls="-",c="blue",lw=1);
plt.plot(x,y2,ls="--",c="red",lw=3);
Marker (Typ , Farbe , Dicke)¶
marker - Markerstil

markevery - Anzahl

ms - Markergröße
Bilder aus: offizielle CheatSheets von Nicolas P. Rougier
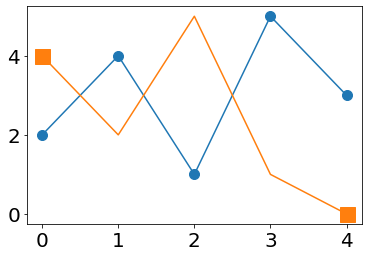
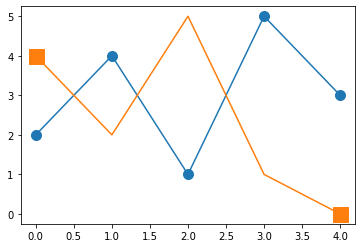
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10);
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1]);
1.4. Beschriftungen¶
Achsenbeschriftung¶
plt.xlabel(" ")plt.ylabel(" ")
bzw.
ax.set_xlabel(" ")ax.set_ylabel(" ")
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10);
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1]);
plt.xlabel("Weg [mm]");
plt.ylabel("Kraft [N]");
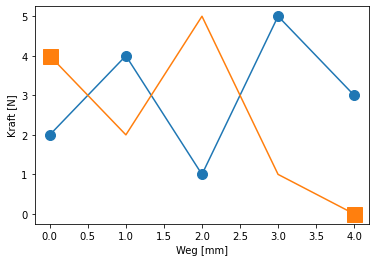
Bildüberschrift¶
plt.title(" ")
bzw.
ax.set_title(" ")
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10);
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1]);
plt.title("Erster Plot");
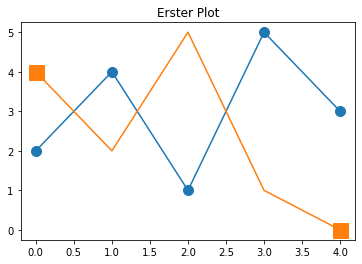
Legende¶
label=' 'Bennenung im plot Befehlplt.legend()Legende anzeigen
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10, label='Messung 1');
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1], label='Messung 2');
plt.title("Erster Plot");
plt.legend();
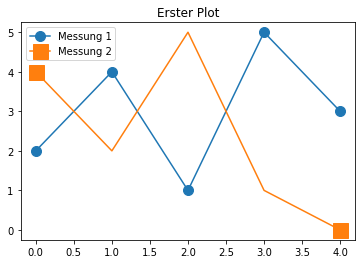
1.5. Wertebereich der Achsen¶
beide Werte vorgeben:
plt.xlim(x1,x2)plt.ylim(y1,y2)
nur einen Wert vorgeben:
plt.xlim(left=x1)oderplt.xlim(right=x2)plt.ylim(bottom=y1)oderplt.xlim(top=y2)
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10);
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1]);
plt.xlim(0,3);
plt.ylim(0,4);
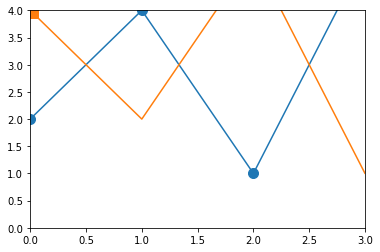
1.6. Gitter¶
plt.grid()
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10);
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1]);
plt.grid();
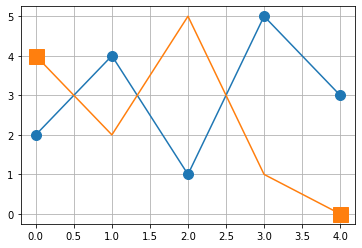
1.7. Bildgröße¶
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5)) - Größe in inces (Default: 6,4)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5));
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10);
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1]);
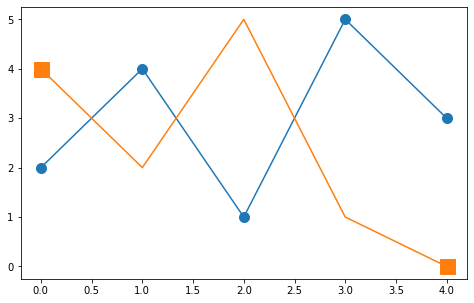
1.8. Schriftgröße¶
global:
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 20})
individuell:
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 20});
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10);
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1]);
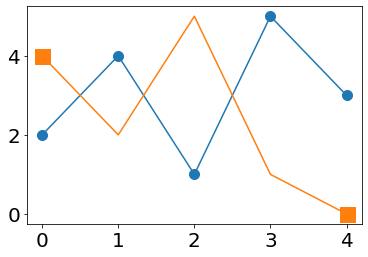
1.9. Bild speichern¶
plt.savefig('Name.png', bbox_inches='tight', dpi=150)
plt.plot(x,y,marker="o",ms=10);
plt.plot(x,y2,marker="s",ms=15,markevery=[0,-1]);
plt.savefig('Name.png', bbox_inches='tight', dpi=150)